Giới thiệu một số nghiên cứu nước ngoài về Sâm Ngọc Linh

1. Nghiên cứu của giáo sư Kazuo YAMASAKI - 1999
BIOACTIVE SAPONINS IN VIETNAMESE GINSENG, PANAX VIETNAMENSIS
Kazuo YAMASAKI
Presented on IOCD-International Symposium as Sattelite Meeting of The Fourth Princess Chulabhorn Science Conbress, 1-2 December 1999, Bangkok, Thailand
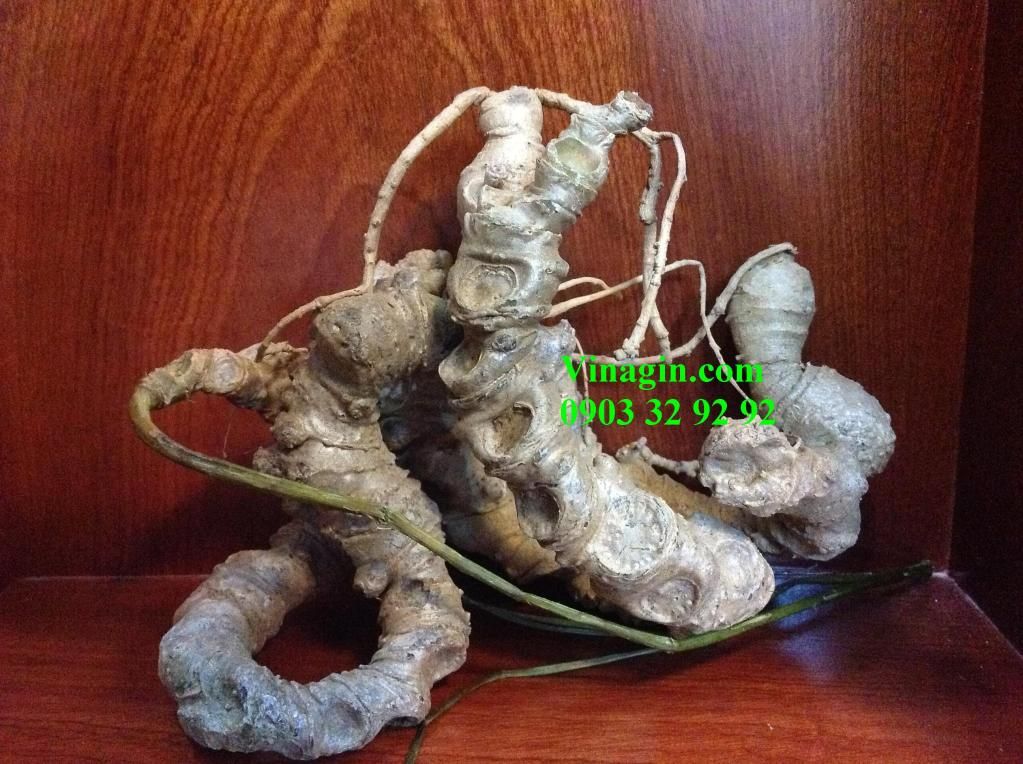
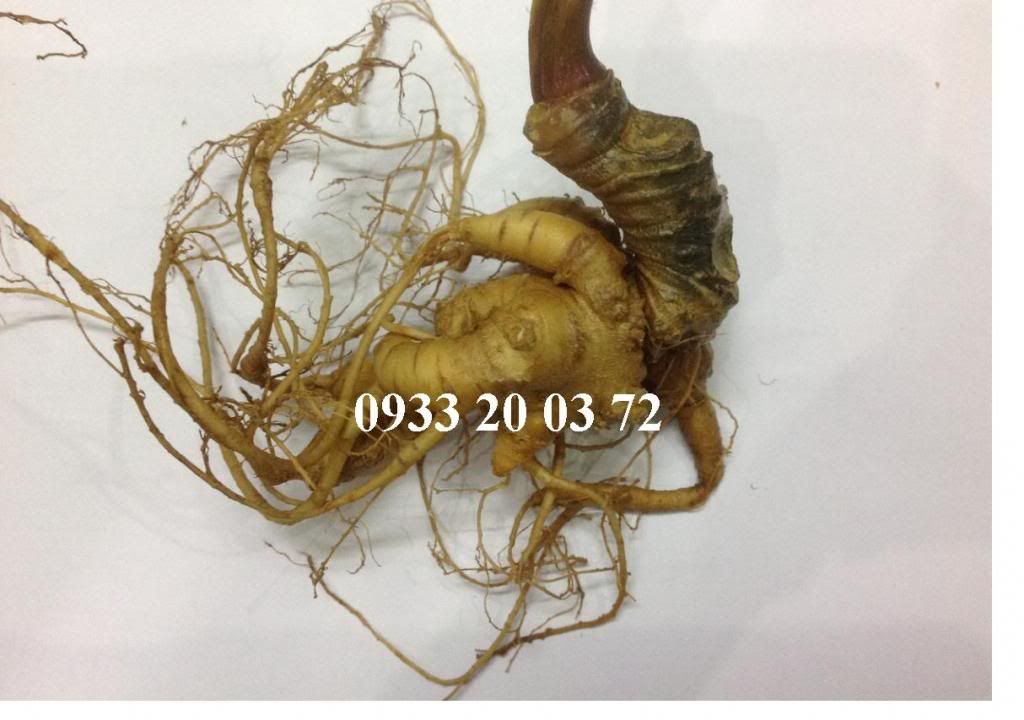
Vietnamese ginseng was found at highland of Central Vietnam in 1973, and was regarded as a new species as Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv (1985). This is the most southern distribution of Panax genus (Araliaceae).
It is a secret medicine of the Sedang ethnic group as a miraculous, life-saving plant drug used for the treatment of many serious diseases and for enhancing body strength in long journeys in high mountains.
 Chemical study on the constituents of the plants clarified 23 saponins including 14 new compounds. Some of them are common to Panax ginseng, such as protopanaxadiol and protopanaxatriol saponins but with higher contents in this species. In addition, extremely high yield of ocotillol saponins, i.e. majonoside-R2 (5.3% of the dried rhizome) were identified.
Chemical study on the constituents of the plants clarified 23 saponins including 14 new compounds. Some of them are common to Panax ginseng, such as protopanaxadiol and protopanaxatriol saponins but with higher contents in this species. In addition, extremely high yield of ocotillol saponins, i.e. majonoside-R2 (5.3% of the dried rhizome) were identified.
We have studied the pharmacological activity of this plant drug in two ways, 1. anti-stress effects and 2. anti-tumor promoting activities, both of which can be attributed to the main saponin, majonoside R2.
(i). Vietnamese ginseng extract attenuated psychological stress-induced antinociception, produced the protective effect against psychological stress-induced gastric lesions, and restored the stress-induced decrease in pentobarbital sleep to the normal level. This action was not observed on Panax ginseng extract. Cumulative findings strongly indicate that majonoside-R2 plays an important role in this effect. The effects of Vietnamese ginseng extract and majonoside-R2 may be mediated by opioid and GABAAreceptor mechanisms.
(ii). Vietnamese ginseng extract showed significant inhibitory activity on Epstein-Barr virus early antigen (EBV-EA) activation induced by TPA. This activity was concentrated to the saponin fraction and especially, major saponin, majonoside R2 exhibited the strongest activity. Flow cytometric study suggested that the activity is ascribable with influencing the cell cycle. The effect of majonoside R2 was confirmed with in vivo test. Two-stage carcinogenesis test of mouse skin tumor caused by DMBA as an initiator indicated the significant decrease of papilloma production prompted by TPA. Also, remarkable inhibitory effect of majonoside R2 on hepatic tumorigenesis initiated with DEN and promoted with phenobarbital was observed.
3. Nghiên cứu của tập thể tác giả: Nguyen Trung Thanh, Nguyen Van Ket, Paek Kee Yoeup
Abstract. We established cell suspension culture on Panax vietnamensis and some attempts have been made to increase ginsenoside yield of ginseng cell culture through manipulation various culture factors and process variable. Half and full strength MS medium were found to be equally suitable for both biomass as well as ginsenoside production. The biomass production and ginsenoside yield were obtained 9.8 g/L DW and 6.81 mg/g DW, respectively. The effect of initial sucrose concentrations were also investigated in suspension cultures of P. vietnamensis for biomass and production of ginseng saponin (secondary metabolite). The final dry cell weight was increased from 5.4 to 10.3 g/L with an increase of initial sucrose concentration from 20 to 50 g/L, but an even higher sucrose concentration of 60 g/L seemed to repress the cell growth, further increase of sucrose concentration upto 70 g/L led to a decrease in ginsenoside accumulation and biomass production. The maximum growth and ginsenoside production was obtained for nitrogen concentration of 30 mM.
Dowload full text: http://www.mediafire.com/?41fzx838tk3zxe6